Defining growth light
1.Growth Light in Horticulture
In horticulture (greenhouses) light is measured in different ways. This can cause confusion, especially when comparing the different units.
| Aspect | Measurement | Range | Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Energy | J or W | 300-3000 nm | Climate control |
| Growth Light | µMol (photons) | 400-700 nm | Plant growth |
| “Visible” Light | Lux | 380-780 nm | Human eye |
2.Growth light measures Unit
Growth light is a measure of potential plant growth (photosynthesis or assimilation rate). Plant growth (Photosynthesis) is determined by the quantity of small light particles (= photons or quantum) from the blue to red (400-700 nm) part of the spectrum. In scientific terms this light is called ‘Photosynthetic Photon Flux (PPF). The more popular term is ‘Growth Light’. A photon or quantum meter measures growth light in µmol (micromole) of photons.
Photosynthesis is determined by the amount of growth light (in µmol/s) absorbed by the leaves.
A measurement of growth light can best be conducted on plant height
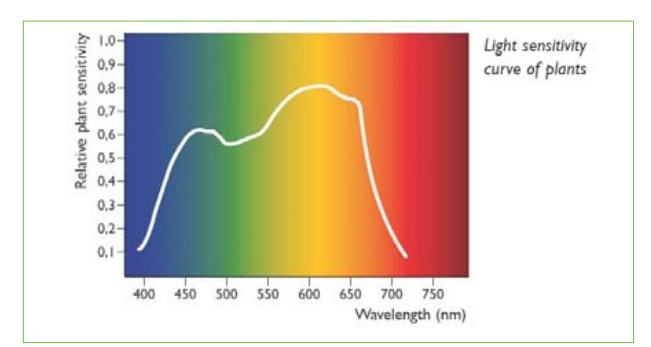
3.Light Sensitivity curve of plants
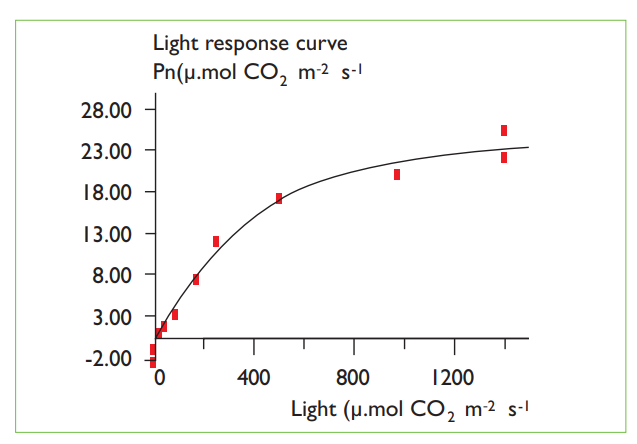
4.Example of a light response curve, measured at a single top leaf of tomato, during winter
 Home
Home Back
Back